
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Select Language
2-N-acetylaminoglycoside is widely distributed in living organisms, often in the form of glycolipids, glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans. In order to better study the mechanism of action of 2-N-acetylaminoglycoside in the process of participating in specific physiological activities, more and more scientists have begun to pay attention to the replacement efficacy and derivative functions of acetylaminoglycan analogs. In recent years, unnatural C-branched deoxysugars have been widely used as synthesizers in the total synthesis of natural products and oligoglycosides, and as ribose analogs have also been involved in regulating cytotoxicity of nucleosides. The study also found that 2-C-acetone-2-deoxysugar, as a carbon branched isostere of 2-N-acetylamino sugar and pharmaceuical intermediate, can be catalyzed by intracellular sugar biosynthetic pathways or extracellular mutant glycosyltransferases , Expressed on cell surface or extracellular oligosaccharides, glycoproteins, peptidoglycans and other glycoconjugates.
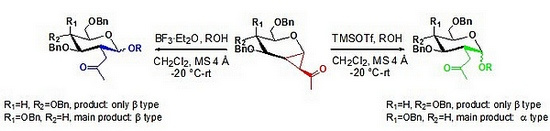
The research group of Shao Huawu, a researcher of the Natural Products Research Center, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the National Research Institute of Canada have conducted systematic explorations in the design, synthesis, and activity of biologically active carbohydrate compounds, and have obtained a series of original research Results. They found that 1,2-cyclopropane saccharides, as sugar donors, can react with a series of sugar acceptors such as oligosaccharides, amino acids and alcohols under the catalysis of Lewis acids to obtain 2-C-branched chains Oligosaccharides and their derivatives. For the galactose donor, when the catalyst is TMSOTf, the α-configuration-based product is obtained; when the catalyst is BF3 · Et2O, the main product is the β-configuration. But for glucose donors, only β-configuration products are obtained under these two conditions. This shows that the activity of the glycosyl donor and Lewis acid determines the stereoselectivity of the glycosylation reaction, which provides a strong basis for its reaction mechanism and chemical raw material. It is inferred from the analysis that the galactose donor undergoes the SN1 pathway under the catalysis of strong Lewis acid (TMSOTf) and the SN2 pathway under the condition of weak Lewis acid (BF3 · OEt2); but for the glucose donor, it only undergoes the SN2 pathway. In addition, the ketal intermediate formed by the 2-C-acetone group and the terminal positive ion also has an important influence on the stereoselectivity of the glycosylation reaction.
Related results have been published in Org. Lett. (2010, 12, 540-543) and J. Org. Chem. (2011, 76, 1045-1053).
January 29, 2024
December 28, 2023
Enviar e-mail para este fornecedor
January 29, 2024
December 28, 2023

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.